Home¶
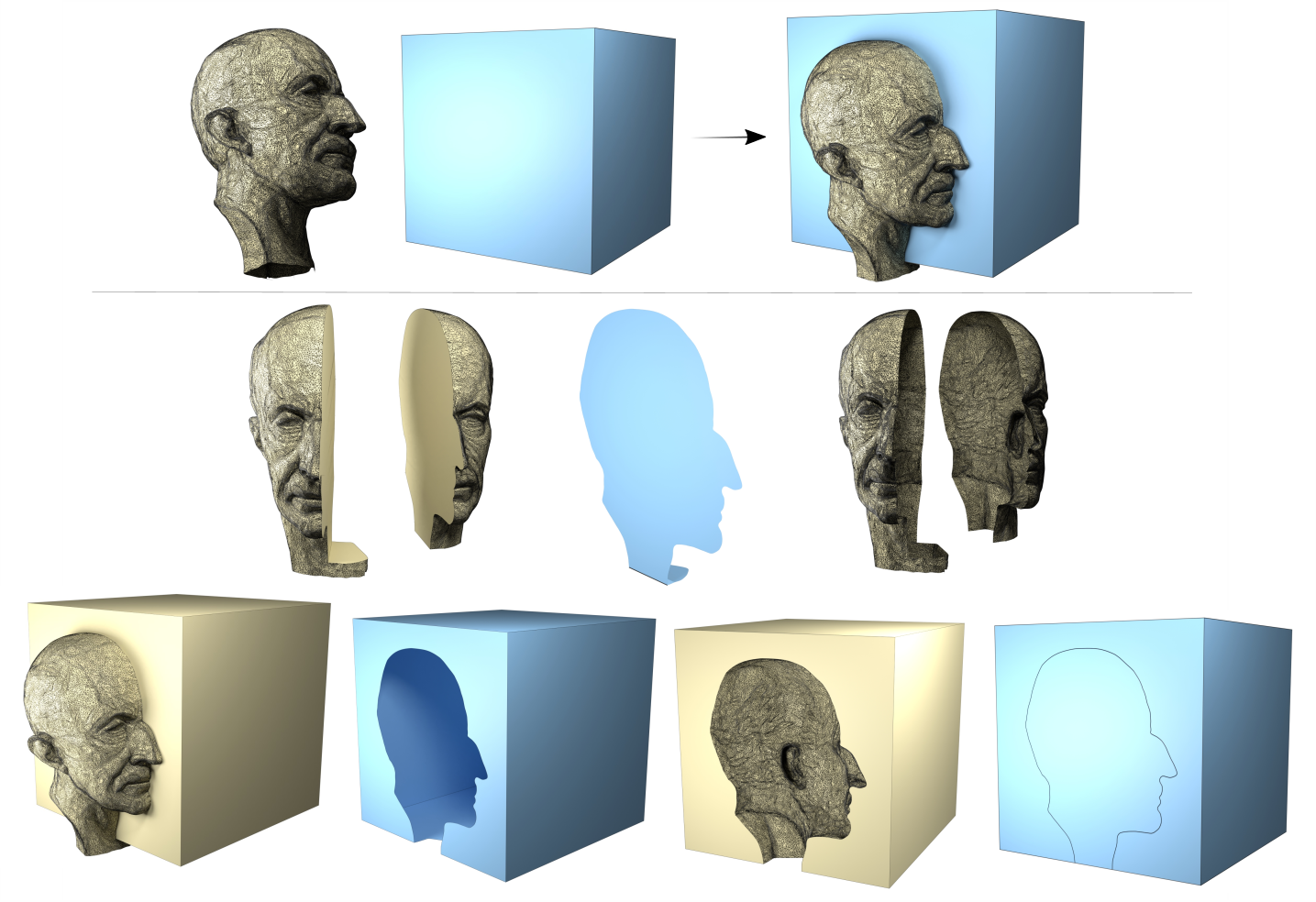

What you can do with MCUT: A Max Planck model cuts a cube.
MCUT (pronounced ‘emcut’) is a tool for cutting meshes: It is a library for partitioning surface-meshes using their geometry to produce crisp fragments at fine scale, which is useful for operations like slicing and boolean operations. Supported features include stencilling (exact cut-outs of the cutting surface), intersection-curve queries and partial cuts. MCUT is a tool providing a general solution to the problem of resolving mesh intersections.
Design principles¶
The design principles of MCUT are as follows:
-
Robust: Thorougly tested.
-
Simple: Easy and portable API.
-
Minimal: Self-contained.
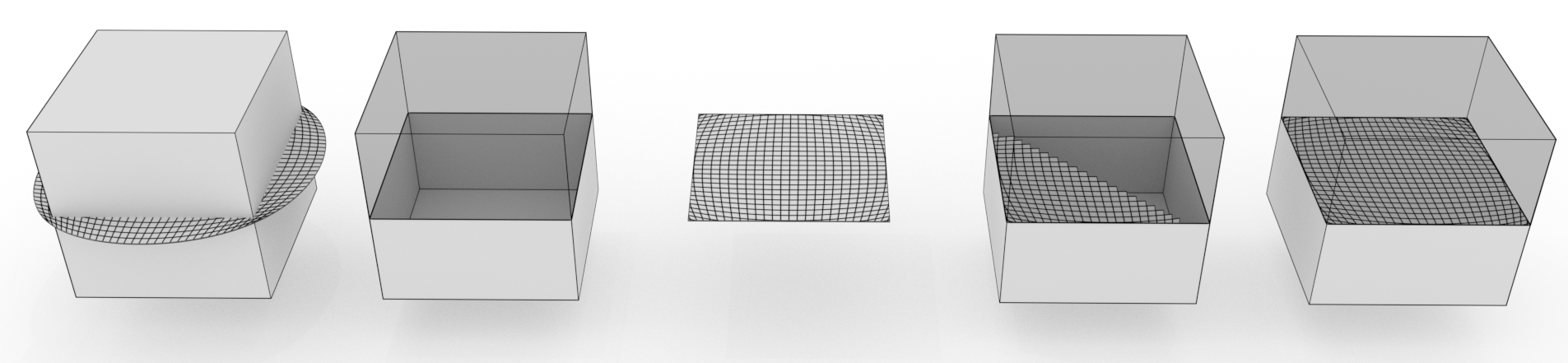
An illustrative gist of what MCUT does: On the left is a cube (the "source mesh") that is cut by a circular surface (the "cut mesh"), which together comprise the input. On the right is the resulting set of connected components after partitioning the cube. In general, the output of MCUT includes unsealed fragments (mid-left), cut mesh patches (middle), and the sealed fragments whose holes have been filled with cut mesh polygons that lie on the interior of the source mesh. Sealing can also be done using cut mesh polygons that lie on the exterior of the source mesh. .
Motivation¶
Mesh cutting is fundamental and useful for solving a wide set of problems. The goal is to split a given surface mesh into a set of disjoint parts using another surface mesh. These resulting parts are typically employed in model design and/or simulation, such as virtual surgery, game level-design, computer aided design and manufacturing.
Despite existing tools (e.g. CGAL, Cork, EMBER, Carve, PWN or TetMesh tools), it remains a challenge to slice meshes without restrictive assumptions on the input. Moreover, besides traditional CSG operations, most sophisticated modelling software (e.g. Maya, Cinema4D, Blender, MeshMixer, ANSYS SpaceClaim etc.) allow users only to cut meshes with a plane which restricts modelling and design capabilities.
Features¶
In addition to being simple and robust, MCUT is specifically designed to be a cutting tool which supports the following features:
- Manifold meshes: open (with borders/boundaries), or closed (as in ‘watertight’ solids).
- Partial cuts: A sliced object need not be completely cut into disjoint parts.
- Stencilling: Silhouette cut-outs of the cutting surface patches.
- Intersection curves: Query vertices introduced as a result of a cut.
- Booleans: Traditional CSG operations.
- N-gons: Arbitrary planar-polygon meshes.
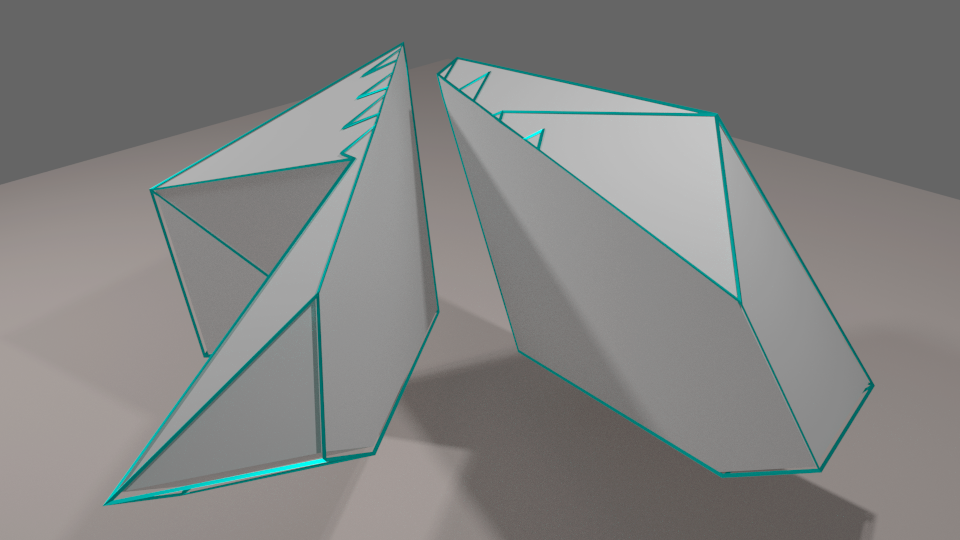
An extreme example, which is a result of cutting a source mesh that has concave polygons. The source mesh was a pentagonal frustum with the pentagons (top and bottom faces) made concave (and not parallel to each other). Each pentagon was composed of polygons with several concavities. The whole model was composed of only one volume element (all edges are on the surface). MCUT produces the correct fragments, and does not modify the connectivity except where intersected with the cut mesh.
Contact¶
MCUT is an endeavor led by Floyd Chitalu via CutDigital Enterprise Ltd. Please write an email if you have questions or comments. For troubleshooting, please post an issue on github.